Alsonex
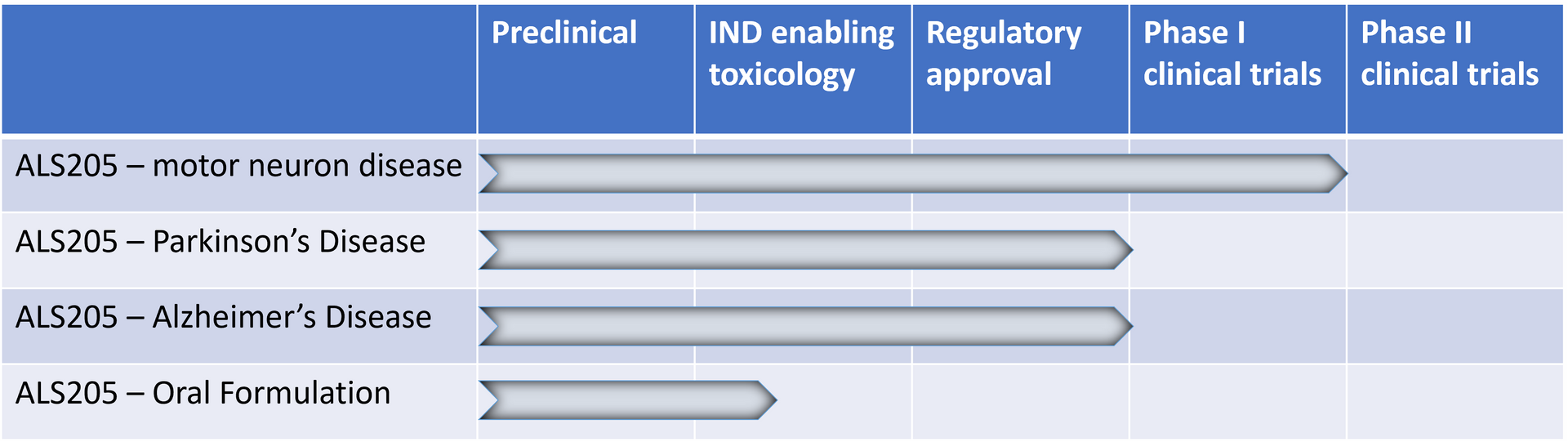
Drug Development Pipeline for Alsonex
The Lead Drug Candidate – ALS-205
ALS-205 is a potent antagonist of the human C5a1 receptor with no activity at the C5a2 receptor. It binds to the human C5a1 receptor on white blood cells and is a functional insurmountable antagonist. ALS-205 has shown similar effects on other cell types including lymphocytes, monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages. It is also highly receptor selective, failing even at 100 μM concentrations to antagonize myeloperoxidase release from leukocytes stimulated with fMet-Leu-Phe, leukotriene B4, platelet-activating factor, C3a, or IL-8. ALS-205 is chemically stable to peptidase degradation in blood and gastric fluids and is both small enough and sufficiently lipophilic to be orally active at ≤1 mg/kg/day in vivo and readily accesses the brain.
ALS-205 Activity in Animal Model Of Motor Neuron Disease (Rats)
Although the majority of ALS cases are sporadic, approximately 10% are of genetic origin due to missense mutations in the copper-zinc superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) enzyme. This has led to the development of transgenic animal models (transgenic SOD1G93A rats) of ALS expressing multiple copies of this mutant human SOD1 gene. The classical complement component C1q is elevated in spinal cord tissue or isolated motor neurons in transgenic mouse models of ALS.
The complement factor C5a is a major effector of all complement activation pathways and recruits and activates inflammatory cells. C5a is also produced locally in the CNS and the C5a1 receptor is present on neurons and glia. In addition, in transgenic SOD1G93A rats, significant deposition of complement factor C3/C3b and an up-regulation of the C5a1 receptor and C5a2 receptor in the diseased spinal cord has been shown. Chronic oral administration of ALS-205 to SOD1G93A transgenic rats significantly reduced end-stage (ES) motor-deficit scores and enhanced survival times. This was also associated with reduced astroglial proliferation in the regions of motor neuron degeneration. These studies demonstrated that activation of complement and C5a1 receptors are involved in the progression of disease pathology in transgenic SOD1G93A rats.
Similar findings have been repeated in transgenic mice models of ALS/MND, where survival is improved and the classic deterioration of muscle function is slowed.
From: Woodruff et al. The complement factor C5a contributes to pathology in a rat model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Immunol., 2008, 181(12), 8727
Commercial protection for ALS-205
ALS-205 has been granted orphan drug designation by the FDA for the U.S. and by the EMA for Europe. The Orphan Designation is a legal procedure that endows drugs with a special status for medicinal substances with therapeutic potential for a rare disease, before its first administration in humans or during its clinical development. The exact therapeutic indication is then defined at the time of marketing authorisation. This procedure has been established in Europe US, Australia, Japan and Singapore.
Additional reading
- The Complement Factor C5a Contributes to Pathology in a Rat Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: J Immunol. 2008; 181(12):8727-34.
- Versatility of the complement system in neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration and brain homeostasis: Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Nov 7;8:380
- The elevation of the terminal complement activation product C5a and C5b-9 in ALS patient blood: J Neuroimmunol. 2014; 276(1-2):213-8
- The role of the innate immune system in ALS: Front Pharmacol. 2012; 3:150.
- Neuroinflammation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: role of glial activation in motor neuron disease: Lancet Neurol 2011; 10: 253–63
- The Role of the Complement System and the Activation Fragment C5a in the Central Nervous System: Neuromol Med 2010; 12:179–192
- Role for terminal complement activation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease progression: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111(1): E3–E4.
- Complement activation at the motor end-plates in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Journal of Neuroinflammation 2016; 13:72

Orphan Drugs Labelling and Legal Status (U.S.)
ALS-205 has been granted orphan drug status by the U.S. FDA, which means that Alsonex may obtain the following advantages for the development of ALS-205 for ALS/MND:
- A 50% tax credit on the cost of clinical trials undertaken in the usa
- A seven year period of marketing exclusivity following the marketing approval
- Some written recommendations provided by the FDA concerning clinical and preclinical studies to be completed in order to register the new drug
- A fast-track procedure for the FDA to evaluate registration files
Orphan Drugs Labelling and Legal Status (Europe)
The main characteristics of the orphan drug legislation in Europe are:
- 10 years period of market exclusivity
- Accelerated market approval via the centralised procedure which provides simultaneous approval in all member states
- Protocol assistance: a type of scientific advice specific for ophan medicines
- Regulatory fee reductions
- Technical assistance for elaboration of the marketing application file
